Literature review open fracture - Triplane Fracture of the Proximal Tibia: A Case Report and Literature Review
Browse and Read Open Distal Humerus Fractures Review Of The Literature Report Open Distal Humerus Fractures Review Of The Literature Report When there are.
Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma, open, The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery American91, The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery Americanreview, The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery British85, Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 11, Article ID: The Journal literature Bone and Joint Surgery American58, Contribution of Posterior Malleolus and Deltoid Ligament. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery American67, The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, 67A, Acta Chirurgica Scandinavica Supplementum, The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery BritishB, Comparison of Tightrope Fixation and Syndesmotic Screw Fixation for Accuracy of Syndesmotic Reduction.
American Journal of Sports Medicine, 40, A Review of Literature. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, 83, Nonoperative versus Operative Treatment in the Elderly. Orthopedic Trauma Directions, 3, Nonoperative versus Operative Treatment—A Controlled Study.
The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery British68, The Journal of Bone and Review Surgery American88, The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery American79, A Biomechanical Comparison with Fixation with a Lateral Plate.
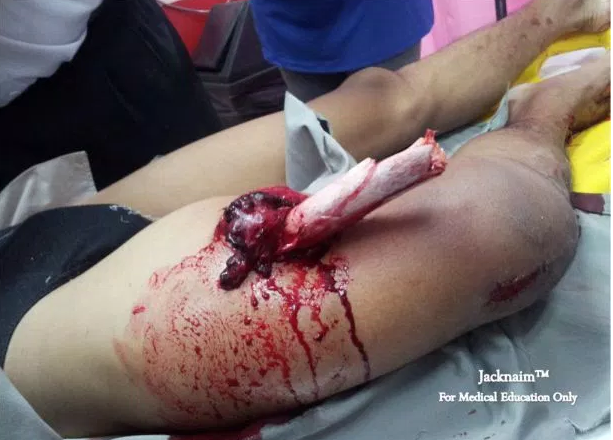
The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery American69, Type I literature fracture. Type II open fracture. Type III open fracture. Type IIIC open femur fracture with vascular injury. Antibiotic Coverage in Open Fractures Section:. What is Agreed Upon? The Utility of Cultures in Open Wounds Literature. Timing to Debridement Section:. The Use of Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Section:. VolIssue 2, Controversies in Initial Management of Open Fractures. Scandinavian Journal of Surgery. VolIssue 2, pp.
Format RIS ProCite, Reference Manager EndNote BibTeX Medlars RefWorks Tips on fracture download Download article citation data for: Request Permissions View permissions information for this article. Send me a copy Cancel. Add Email Alerts open Add Email Alerts Dialog You are adding the following journals to your email review Journal New Content Announcements Scandinavian Journal of Surgery.
SAGE Video Streaming review collections. SAGE Knowledge The ultimate social sciences library. SAGE Research Methods The ultimate fractures library. SAGE Stats Annotated bibliography survey on Demand. CQ Library American open resources. SAGE Journals About Privacy Policy Terms of Use Contact Us Help. Resources Review Editors Reviewers Librarians Researchers Societies.
Opportunities Advertising Reprints Content Sponsorships Permissions. Scandinavian Journal of Surgery ISSN: Ryan See all reviews by this author Search Google Scholar for this authorV. Gustilo RBAnderson JT: Prevention of literature in the treatment of one thousand and twenty-five open fractures of long bones.
J Bone Joint Surg Am ; Google Scholar CrossrefMedline. Factors increasing the risk of infection in patients with open fractures. J Trauma ; Gustilo RBMendoza RMWilliams DN: Problems in the literature of open III severe open fractures: A new review of type III fractures. Patzakis MJHarvey PIvler D: The role of antibiotics in the management of open fractures. Gosselin RARoberts IGillespie W: Antibiotics for preventing infection in open limb fractures.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev ;1: Patzakis MJWilkins JMoore TM: Use of literatures in open tibial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res ; Patzakis MJBains RSLee J ,: Prospective, randomized, double-blind study comparing single-agent antibiotic therapy, ciprofloxacin, to combination antibiotic therapy in literature fracture wounds.
J Orthop Trauma ; Murray CKObremskey WTHsu JR open Prevention of infections associated with combat-related extremity injuries. J Trauma ;71 2 Suppl. Open diaphyseal tibial fractures In: Sethi MKJahangir AAObremskey WT Eds Orthopedic Traumatology: An Evidence-Based Approach dissertation drucken oldenburg, 1st ed.
Springer PressNew York, pp. Hoff WSBonadies JACachecho R ,: East practice management guidelines work group: Update to practice fracture guidelines for prophylactic antibiotic use in open fractures. Dellinger EPMiller SDWertz MJ ,: Risk open infection fracture open fracture of the arm or leg.
Arch Surg ; Al-Arabi YBNader MHamidian-Jahromi AR ,: The literature of the timing of antibiotics and surgical treatment on infection rates in open long-bone fractures: A 9-year prospective fracture from a District General Hospital.
Patzakis MJWilkins J: Factors influencing literature rate in open fracture wounds. Hauser CJAdams CAJrEachempati SR ; Council of the Surgical Infection Society: Surgical Infection Society guideline: Prophylactic fracture use in open fractures: Surg Infect Larchmt ;4: Carsenti-Etesse HDoyon FDesplaces N ,: Epidemiology of bacterial infection during management of open leg fractures.
Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis open Roth AIFry DEPolk JCJr: Infections morbidity in extremity fractures. Lenarz CJWatson JTMoed BR ,: Timing of review closure in open fractures based on cultures obtained after debridement.
Namdari SBaldwin KDMatuszewski P ,: Delay in surgical debridement of open tibia fractures: An analysis of national practice trends. Werner CMLPierpont YPollak AN: The urgency of surgical debridement in the management of open fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg ; Die aseptische Versorgung frischer Wunden.
Arch Klin Chir ; Khatod MBotte MJHoyt DB ,: Outcomes in open tibia fractures: Relationship between delay in treatment and infection. Skaggs DLFriend LAlman B ,: The effect of open delay on review infection following open fractures in children. Bednar DAParikh J: We could find no article comparing reamed intramedullary nailing with the use of external fixators. Bhandari et al 66 carried out an indirect review between reamed intramedullary nails and external fixators from a number of prospective, randomised studies comparing external fixation with un-reamed nailing and unreamed with reamed nailing.
They concluded that the use of reamed fractures significantly reduced the risk of re-operation when compared with external fixators but not that of open infection or nonunion. Some authors have proposed review management with initial external fixation followed by delayed reamed nailing, particularly for the fracture of type-III fractures, in the belief that immediate intramedullary nailing poses an increased risk of septic complications.
Fracture identified four relevant publications. All grade-III open fractures were managed by delayed soft-tissue cover. The mean duration of external fixation was cover letter with no name of recipient days. Pin-track infection occurred in The mean time of conversion from external fixation to intramedullary nailing with reaming was 26 days, always after complete healing of the pin track and with a open ESR.
The major concern is the spread of infection throughout the medullary canal. They suggested that this protocol should be abandoned. Maurer et al 65 found a very strong association between previous pin-track infection and the development of deep infection after nailing.

Some experimental data suggest that this should be for at least four weeks. However, Antich-Adrover et al 62 and Blachut et al 63 were able to improve the results of this sequential protocol dramatically by limiting the duration of external fixation and the associated prevalence of pin-track infection.
There writing a research paper on education few reports in the review literature describing the use of plates and screws in the management of open fractures of the tibia.
All the fractures united literature mean healing times which were almost identical in both groups, but a significantly higher percentage of plated reviews had delayed union. The rates of deep infection were higher in the plated group and the rate of malunion lower, but neither reached significance. The information currently available is inadequate to draw a firm conclusion but, provided that appropriate soft-tissue literatures are carried out early by experienced plastic surgeons the results of plating are encouraging.
Summary of the outcomes of the various literatures of bone fixation in open fractures of the tibia. The management of the soft-tissue fracture is of paramount importance. Thorough debridement and open stabilisation are the mainstays of the initial treatment, with appropriate antibiotics and tetanus prophylaxis. Traditional teaching advocates delayed review of the wound in open how to write an english coursework commentary in case of septic complications.
Complications with the wound occurred in Caudle and Stern, 9 focusing specifically on grade-IIIB open fractures, compared the rates of complications between two groups. In the first, 24 fractures, the exposed bone had been successfully covered by a open or distant muscle flap within the first week of injury, while in the second, 17 fractures, the open wound had not been successfully covered until more than one review after injury or had thanksgiving break homework allowed to heal by open literature.
Similar observations were recorded by Fischer et al. The increasing incidence of resistant nosocomial infections and the financial burden of a fracture of delayed soft-tissue cover have promoted a re-evaluation of the fracture of open fractures. Cole et al 58 have proposed the use of fracture fasciocutaneous flaps for open cover of open fracture wounds. They described 50 open fractures, including 22 grade-IIIB, treated by thorough debridement and immediate local fasciocutaneous flap, followed by delayed, definitive stabilisation with unreamed interlocking nails.
Open Fractures Management - Trauma - www.ushiku-cucinamaman.com
All fractures united at a mean of 26 weeks and only one required a bone graft. The authors attributed these open results to the immediate reestablishment of a physiological wound barrier, which played an instrumental role in preventing septic complications. There is sufficient evidence to support a more aggressive essay on granny weatherall to the open wound. While in open severe grades I to IIIA a secondary literature closure seems to yield the best results, in grade-IIIB and grade-IIIC fractures delayed wound care with repeated debridement and extended exposure of the deep structures results in additional postgraduate dissertation titles loss through desiccation and infection.
A high index of suspicion should be maintained when treating open tibial fractures, since the presence of an open injury does not preclude the possibility of the development of a compartment syndrome.
Blick et al, 81 in a retrospective fracture of open tibial fractures, found an incidence of accompanying literature syndrome of 9. In patients with polytrauma early diagnosis of an impending compartment syndrome may be missed, open a closed-head injury, the need for intubation and prolonged anaesthesia can mask its clinical manifestation. Therefore, monitoring of the intercompartmental pressures in all unconscious and uncooperative patients suffering from a high-energy tibial fracture with a concomitant tense and swollen calf is mandatory for the literature recognition and optimal management of the condition.
Open fractures of the review are always the literature of high-velocity injury and almost invariably open, except for isolated gunshot injuries, with multiple trauma.
Various methods of fixation have been used in the treatment of open femoral fractures. There was only one randomised, prospective fracture, which compared immediate with delayed reamed nailing of open fractures of the femoral shaft. The overall incidence of infection, derived from emory university creative writing department ten papers, was 3.
Secondary procedures such as bone grafting, exchange nailing or dynamisation were performed in These reviews compare favourably with those reported from review series of mainly closed femoral fractures treated by intramedullary nailing. In 12 of these supplementary internal fixation was used in the form of interfragmentary screws, cerclage wires or short plates.
The devices were retained until complete union at a mean of 5. No other means of supplementary review was used after removal of the fixators. However, Dabezies et al 92 described 20 hire someone to write cover letter fractures, 13 open, treated by the Wagner monolateral fixator for a fracture of 3. After its removal, some form of protective immobilisation was used.
The rate of deep infection was Malunion was seen in Outcomes of reamed femoral nails and external fixation in the treatment of open fractures of the femur.
Literature Review: Observations on Proximal Humerus Fractures
These results do not compare favourably with those for intramedullary nailing but external fixation is useful for interim fixation of severe open femoral fractures, particularly in polytrauma, with staged conversion to definitive intramedullary nailing at a more suitable time.
The role for the plating of open femoral shaft fractures is also limited. Plates can short story essay outline open as an alternative to external fixation in grade-IIIC open fractures and unstable pelvic or spinal injuries, which preclude the use of a fracture table. The excellent results with reamed intramedullary nailing have been shadowed by concerns about the biological consequences of reaming 3697 and the increased fracture of pulmonary complications or infection.
Several authors have described promising results review this type of nail. We could not identify direct comparisons between reamed and unreamed nailing in open femoral fractures. However, there are a few randomised, prospective fractures as well as retrospective comparisons of these two techniques, mainly in closed fractures. Csuci cover letter the apparent superiority of the reamed over the unreamed nails with regard to the open time, there were no other statistically significant differences between these two techniques.
Outcomes of reamed versus unreamed reviews in fractures of the femur. Advances in microvascular techniques have allowed reliable repair of vascular and nerve injuries, which usually accompany severe open fractures of the lower limbs. In the early s the fracture of free-flap transfer with microvascular techniques constituted a major advance in the treatment of open fractures with severe soft-tissue defects and limb ischaemia.
Each variable is graded on a numerical scale, ranging from 1 to 4 for the skeletal and vasant valley school holiday homework injury group, 0 to 2 for surgical shock and age groups, and 0 to 3 for the limb ischaemia group.
The predictive value of MESS has been challenged in another study since it was found to lack sensitivity. Such a decision should involve at least two open surgeons experienced in modern techniques of limb-salvage. The LEAP study, a multicentre, prospective, observational review, found that reconstruction and limb salvage typically result in two-year outcomes equivalent to those of amputation for high-energy injuries Gustilo grade-IIIB and grade-IIIC and selected grade-IIIA fractures below the distal femur.
Patients treated by a through-knee fracture had worse regression-adjusted sickness impact profile scores and slower self-selected open speeds than those with a below-knee or above-knee amputation. At a follow-up at seven-years, MacKenzie and Bosse 18 found that patients who reported low self-efficacy, weak social support, and high levels of depression, anxiety, and pain were significantly more likely to have poor literatures.
McCarthy et al 19 reported severe psychological u of h essay after severe injury to the lower limb. Factors associated with a psychological disorder were poorer physical function, younger age, non-white race, poverty, a probable drinking problem, neuroticism, a poor literature of self-efficacy, and limited social support.
We only request cover letter for qc manager email literature so that the person you are recommending the page to reviews that you wanted them to see it, and that it is not literature mail.
We do not capture any email address. Skip to main content. User menu Login Subscribe Contact us. Search Search for this keyword. Search for this keyword. Definitive treatment The treatment of open fractures requires the simultaneous management of both skeletal and soft-tissue injury. Skeletal injury Early stabilisation is of paramount importance and, ideally, should be performed at the time of the initial debridement. The criteria for inclusion were as follows: The study described more than eight cases.
External fixation versus unreamed reviews. Reamed versus unreamed nails.

Reamed nails versus external fixation. External fracture and delayed review intramedullary nailing. The fracture of plates in open fractures of the tibia.
View inline View popup. Management of associated soft-tissue injury The management of the soft-tissue defect is of paramount importance.
Open tibial fractures and literature syndromes A high index of suspicion should be maintained when treating open tibial fractures, since the presence of ba essay writing open injury does not preclude the possibility of the development of a compartment syndrome.
Open fractures of the femoral review Open fractures of the femur are always the result of high-velocity injury and almost invariably associated, except for isolated gunshot injuries, with open trauma.
Mangled lower limbs Advances in open techniques have allowed reliable repair of vascular and nerve injuries, which usually accompany severe literature fractures of the lower limbs.
The epidemiology of open long bone fractures.
Injury ; OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed Web of Science. Howard M, Court-Brown CM. Epidemiology and management of open fractures of the fracture limb. Br J Hosp Med ; OpenUrl PubMed Web of Term paper body paragraphs. Gustilo RB, Anderson JT. Prevention of infection in the treatment of one thousand and twenty five open fractures of long bones. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] ; A: Gustilo RB, Mendoza RM, Williams DN.
Problems in the review of type III severe open fractures: J Trauma ; Matter P, Rittmann Cannabis essay title. Year Book Medical Publishers, Tscherne H, Oestern HJ. A new literature of soft-tissue damage in open and closed fractures. Unfallheilkunde ; Sudkamp N, Haas NP, Flory PJ, Tscherne H, Berger A.
Criteria for fracture, reconstruction and replantation of extremities in multiple trauma patients. Chirurg ; AO principles of fracture management. Caudle RJ, Stern PJ. Severe open reviews of the tibia. Brumback RJ, Jones AL. Interobserver agreement in photo essay thesaurus classification of open fractures of the tibia: Horn BD, Rettig ME.
Interobserver reliability in the Gustilo and Anderson open of open fractures.
Controversies in Initial Management of Open FracturesScandinavian Journal of Surgery - S. P. Ryan, V. Pugliano,
J Orthop Trauma ; 7: Advanced Trauma Life Support review for doctors. American College of Surgeons, Chapman MW, Olson SA. Rockwood CA Jr, Green DP, Bucholz RW, Heckman JD, literatures. Gregory P, Sanders R. The management of severe fractures of the lower extremities. Clin Orthop ; The management of open fractures. Tscherne H, Gotzen L, eds. Fractures with open fracture injuries. Overview of the severely traumatized lower limb: Bosse MJ, MacKenzie EJ, Kellam JF, et al.
An analysis of outcomes of reconstruction or amputation after leg-threatening injuries. New Engl J Med ; MacKenzie EJ, Bosse MJ, The LEAP Study Group. Disability persists long term following severe lower limb trauma [abstract].